BIO INTERNATIONAL 2023: A Lively Life Science Gathering

On June 7, 2023, I was privileged to cover the convention of the Biotechnology Industry Organization (BIO) International Convention–my first time attending the meeting since 2018, when the 25th anniversary of the gathering was held here in Boston. The excitement was back–with 9144 companies registered to attend, many with booths, tables or pavilions–and, according to Stat News, some 15, 000 investors, executives and promoters.

On the afternoon of its third day, the convention, headlined “Stand Up for Science,” had a more fun and friendly vibe than I’d noticed at past BIO conventions.
Short on time, I wandered around the exhibition floor–chatting with exhibitors and attendees, snagging a latte, dark chocolate squares, a small nylon backpack advertising New York State Life Sciences, and a large mousepad.
I was sorry to miss many fascinating discussions: “Realizing the Promise of Gene Therapy and Gene Editing: Current Challenges, Opportunities and Trends; ” “A Price Control Odyssey: The Inflation Reduction Act’s Effects on the Innovation Ecosystem;” ” Belonging in Biotech: How to Advance Greater Inclusion Across the Biotech Workforce;” “Launching Successful Gene Therapies; Fighting Antimicrobial Resistance with Vaccine Innovation; ” “New Approaches to Oncology Drug Discovery;’ Re-imagining Drug Development and Regulatory Submissions through Cloud-Based Technologies;” “The Intersection of Cancer and Mental Health”; “Women and their Health: Fueling an Ecosystem of Scientific Innovation to Address Unmet Needs”. All of the above (and more) took place in the same hour as my first chosen panel discussion of the day: “Psychedelics…the Trip Continues.” (I viewed a streaming version because the main conference room was packed full.)
Psychedelics…the Trip Continues
Freelance journalist and broadcaster David Cox led Jeff Rolx, venture partner and portfolio CEO at 02h Ventures; Kurt Rasmussen, Chief Scientific Officer at Delix Therapeutics, Inc., and Peter Silverstone, CEO and Director of Zylorian Health in a wide-ranging discussion of the future an evolving industry projected to be worth billions of dollars, one day.

The panelists described the variety of challenges faced by the fledgling industry as it evolves from what the official writeup termed “a stigmatized counterculture” to a scientifically robust industry.
Among the challenges:
- Navigating the wide variety of regulatory systems in the US and abroad as well as attitudes of different states and national governments
- Issues involved in clinical trials given potentially dangerous side effects; measuring efficacy of treatments when placebos are not an option
- Whether the pharmaceutical industry will invest in a field with a “hippy” reputation
- Whether non-hallucinognic forms will be likelier to be used therapeutically before hallocinogenics
- How psychedelic therapeutics will get to market given the difficulty small developers may have in getting funding
- Determining what the therapy is and how it can be standardized.
“We are completely blind right now, ” said Silverstone, of Zylorian Health. “Our AI [artificial intelligence] overlords may soon tell us [what to expect]…but we are just at the beginning.” Silverstone predicted that the next three or four years will be telling for the industry, and suggested that 2024 could possibly be “a big year” for psychedelics.
Roix, of 02 Ventures described the current mental health situation as a “public health emergency,” with huge numbers of patients struggling with depression and post traumatic stress disorder. There are complex protocols and treatments and too few resources, he said. He also wondered how anyone will make money–especially if psychedlics work after just a few treatments and are not given as pills to be taken every day.
According to Silverstone, science is moving to the point where “the opportunity to deliver something novel in the field of neuroimmunology is huge.”
He predicted that the field may need to be “reformatted” to interest big pharma–“which will jump in when it’s ‘de-risked’ from safety concerns, reimbursement issues and questions about whether non-hallucinogens will work.
Rassumen of Delix Therapeutics expressed optimism that non -hallucinatory forms are possibilities. He pointed out that that compounds that enhance structural nerve plasticity are “starting to uncover how the brain changes over time”–which could, perhaps in conjunction with stem cell therapies, lead to getting back some functions in patients with dementia and other diseases of the aging brain.
He also said that treatment forms which resemble what in past would have been called “tripping” may diminish because depressed patients now seem to be more secure in carefully monitored medical settings.
When Rasmussen suggested possibly rebranding the field–that is, ” don’t call it psychedics,” Silverstone quipped, “That won’t happen.”
Life Science and the Gun Violence Epidemic
I next attended “The Life Sciences Industry: Taking a Public Health Approach to Ending the Gun Violence Epidemic,” moderated by Steve Usdin, Washington Editor and Head of Policy and Regulation at BioCentury.
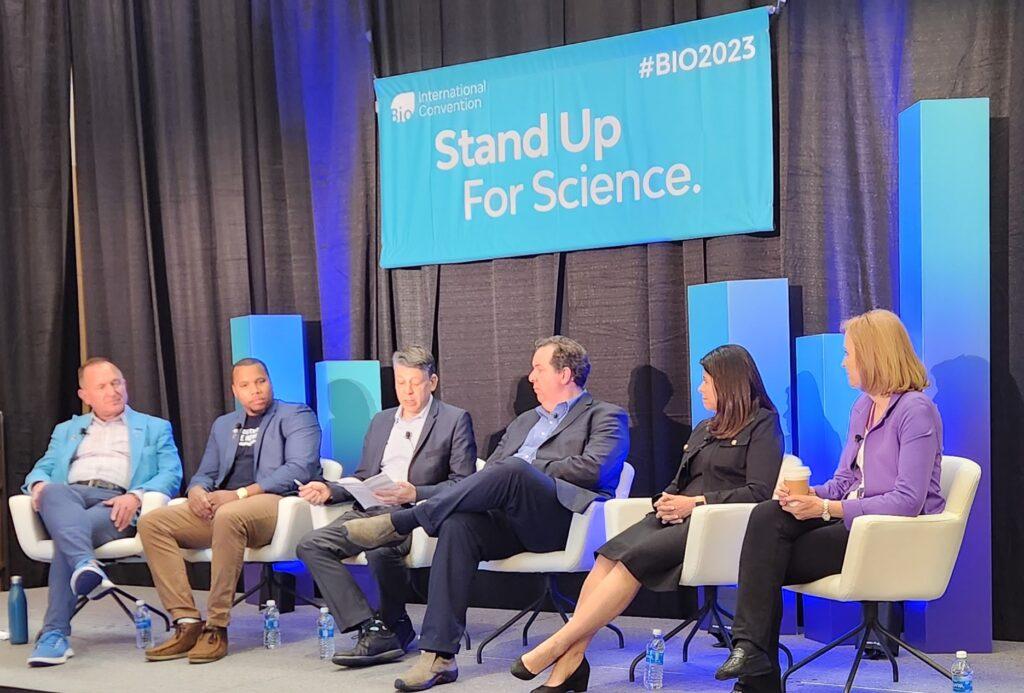

The panelists included (left to right) Paul Hastings, President and CEO of Nkarta, a clinical stage biotechnology company in California; Juan Carter, outreach manager at the Giffords Center for Violence Intervention, headquartered in San Francisco and Washington, DC. [moderator Steve Usdin] ; Angus Mcquilken, co-founder of Life Sciences to End Gun Violence Epidemic and Industry Relationship Executive for Life Sciences at Boston Law Firm McDermott Will and Emery; Sharon Barber-Lui, a life sciences leader and BIO board member; and BIO CEO Rachel King.
All of the panelists said they strongly believe in gun control; King and Barber-Lui both said they had attended the Million Mom March to call for stricter gun control some twenty years ago. But most agreed that corporate lobbying for what has become a volatile political issue presents difficulties–and that individual commitment is called for.
King said that though she personally supports ending gun violence, she must adhere to the BIO directors’ decision to limit activities to those directly concerning the biotechnology industry.
Mcquilken urged attendees to join the organization he cofounded– “Life Sciences to End the Violence Epidemic”–which lobbies for stronger gun control laws. He pointed out that biotech seeks evidence-based solutions to problems–and that there is strong evidence that Massachusetts’ strict gun control laws, which require considerable training before guns may be purchased, account for the commonwealth’s relatively low rate of shooting deaths.
Hastings said that as a CE0 he has held events supporting gun control measures–but that he has been reticent to publicize photos of participants due to the negative backlash he would expect.
Carter said that it is important for health care and other professionals who work with victims of gun violence and their families to be supportive and accepting of them, lest they become dejected and hopeless when they return to troubled communities, and do not return for needed help.
Also suggested was that companies seeking to recruit youthful employees find ways to encourage activism.
An audience member who did not give his name pointed out that the Second Amendment to the Constitution, which grants certain rights to bear arms , was meant to prevent imperialism but it is now being used to promote terrorism.
Targeting Success: 3 MIT Thought Leaders on Innovation
At my third panel discussion of the afternoon, MIT’s Angela Koehler, associate professor of biological engineering; Robert Langer, David H. Koch Institute Professor, and Giovanni Traverso, associate professor, delved into questions and challenges for scientists in academic and research institutions who seek to bring their innovations to market.
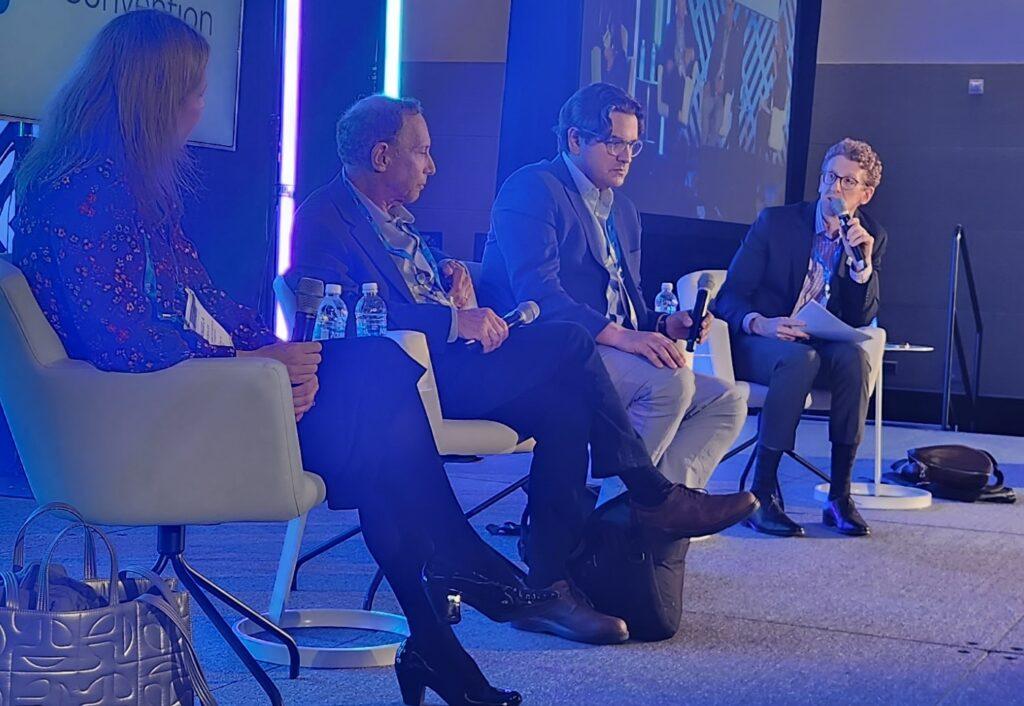

In a discussion moderated by Joshua Fox of the Mintz law firm, Langer [second from left]–who is well- known as a co-founder of Moderna pharmaceuticals and has more than 400 patents licensed or sub-licensed by a myriad of companies–said that spinning a successful company out of academe requires a “breakthrough technology platform”; a really good CE0; and raising enough money. (Full disclosure: Bob is a personal friend of mine).
Koehler [left] emphasized the importance of building “connections” to raise funds and recruit a great team–and that a CEO has to be willing to “plug in a fridge”–that is, be willing to do everything.
According to Travers [second from right], ” it’s important to have a management team as outstanding as the scientific team.” When Langer’s warned not to try to leave the academic setting too early lest you wind up in “the valley of death” (unable to raise enough money), Travers recommended seeking grants and non-traditional investors such as insurance companies to take the science through clinical trials. Koehler suggested looking for disease-oriented foundations for funding.
All-in-all, BIO 2023 a fascinating convention; next time I’ll try to go to everything–which is, of course, impossible.
—Anita M. Harris
Anita Harris is a writer, photographer and communications consultant. She has authored three non-fiction books.
New Cambridge Observer is a publication of the Harris Communications Group, a PR and digital media firm based in Cambridge, Mass.